Human cyclic guanosine monophosphate immunoassay
(Germany IBL CM581021)
expected usage
This enzyme-free kit is used for quantitative detection of cGMP in cell lysates, tissues, plasma and urine.
Experimental principle
This kit employs a competitive enzyme-free method in which free cGMP and acetylcholinesterase-labeled cGMP co-competitively bind to a certain amount of cGMP-specific rabbit antibodies. Since the amount of cGMP labeled does not change, the labeled cGMP binds to the rabbit anti-binding with the difference in free cGMP, and the amount of binding is inversely proportional to the concentration of free cGMP in the well. The rabbit anti-cGMP complex is then combined with the murine monoclonal antibody anti-rabbit IgG previously coated in the microplate, the plate is washed away to remove the unbound complex, and then the substrate coloring solution is added, and the reaction solution has a distinct yellow color. There is a strong absorbance value at 412 nm, and the color development intensity is directly proportional to the bound labeled cGMP concentration, and inversely proportional to the free cGMP.
Kit composition
Numbering | ingredient | 96 holes | 480 holes |
481022 | Antiserum | 1 | 1 |
481020 | Acetylcholinesterase | 1 | 1 |
481024 | Standard | 1 | 1 |
400060 | Buffer concentrate (10X) | 2/10ml | 4/10ml |
400062 | Wash buffer concentrate (400X) | 1/5ml | 1 / 12.5ml |
400035 | Tween 20 | 1 / 3ml | 1 / 3ml |
400004 | Mouse anti-rabbit IgG coated plate | 1 block | 5 blocks |
400012 | Cover | 1 block | 5 blocks |
400050 | Ellman's reagent | 3 pieces / 100dtn | 6 pieces / 250dtn |
400031 | Anhydrous acetic acid | 1 / 2.5ml | 1 / 12.5ml |
400029 | KOH | 1 | 1 |
400040 | Tracer dye | 1 | 1 |
400042 | Antiserum dye | 1 | 1 |
Materials required for the experiment but not provided in the kit
1. Microplate reader 405-420nm
2. Adjustable pipettes and reusable pipettes
3. Ultrapure water
4. Other equipment for sample preparation
Storage conditions and stability
This kit should be stored at -20 °C according to the specified requirements and used within the validity period.
Preparation before experiment
Buffer preparation
All buffers are stored at 4 ° C to 2 months
EIA buffer preparation
Dilute one EIA buffer (No. 400060) with 90 ml of ultrapure water. Make sure to rinse off the salt deposits in the bottle.
Washing liquid preparation
Dilute 5 ml of 400 times concentrated washing solution (96T kit, number: 400062) with 2L of ultrapure water, add 1 ml Tween 20 (No. 400035) or dilute with 1L of 5L ultra-pure water 12.5 ml 400 times concentrated washing Liquid (400T kit, number: 400062), add 2.5 ml Tween 20 (number: 400035)
Tip: Since Tween 20 is a viscous liquid, it cannot be pipetted with a conventional pipette. It needs to be quantified with a displacement pipette and a syringe.
Sample preparation
In general, urine and tissue supernatants can be diluted with buffer and then added directly to the microwells. Plasma, serum, whole blood and tissue homogenates and other non-uniform matrices may contain impurities from the infection test, and it is best to perform interference checks when performing large sample tests. When performing the interference detection test, dilute 1 to 2 test samples, each sample has two different dilution ratios. If the samples with two different dilution ratios have good correlation in the final cGMP concentration calculation, no purification is required. Otherwise purification is required. Since most samples contain phosphodiesterase, the sample is purified by a forced enzyme to hydrolyze cGMP.
Plasma (serum) purification
500 ul of plasma was mixed with 2 ml of ice ethanol, left at room temperature for 5 min, centrifuged at 1500 x g for 10 min to remove the precipitate, and the supernatant was transferred to another 10 ml clean test tube. The supernatant is dried in a vacuum centrifuge or a stream of nitrogen, and then 500 μl of EIA buffer is added (the centrifuge can be used to dry the water in the extract) to ensure that the ethanol has been removed to prevent traces of ethanol from affecting the test results.
Medium sample
Tissue and cell supernatants can be used directly in the assay without purification. If the cGMP concentration in the sample is sufficiently high, a 10-fold dilution with buffer is required and no changes are required for the test operation. When the sample is at a low concentration (the sample is not diluted with buffer), the standard curve in the same medium is diluted to achieve a match between the sample and the standard matrix. We recommend that you first establish a standard curve to ensure that testing can also be performed in a particular sample.
Cell liquid extraction
Proposed medium
2. Add 1 ml of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid per 35 cm 2 surface area.
3. Incubate for 20 min at room temperature
4. Scrape the cells from the surface with a spatula
5. Mix with a pipette until the supernatant is even and transfer to a suitable centrifuge tube.
6. 1000xg
These supernatants can be used directly for testing
Tissue sample
7. The circulating nucleotides in the tissue will be immediately decomposed and centrifuged for 10 min.
1. After the supernatant is poured into another clean test tube, it should be frozen immediately after sampling.
2. Weigh the frozen tissue, add 5-10 units (liquid / ml, tissue / g) of TCA, and mix the sample with a homogenizer.
3. Centrifuge at 1500xg for 10min, remove the precipitate, and move the supernatant to another clean test tube.
4. Extract the TCA from the sample with water-saturated ether. 5 volumes of diethyl ether and 1 volume of the supernatant were mixed for 10 seconds, extracted and separated, and the upper layer was removed, and the extraction was repeated twice or more.
5. Remove the remaining ether by heating the sample at 70 °C.
The supernatant extracted from the tissue was directly used for the test without dilution, and the preparation of the standard curve substrate solution was carried out by extracting 10 ml of 5% TCA treated with diethyl ether, and removing the remaining diethyl ether by heating, and the remaining solution was subjected to a standard curve.
Preparation of specific reagents
cGMP AChE tracer
100dtn cGMP AChE tracer with 6ml buffer
Or 500 dtn cGMP AChE tracer with 30 ml of buffer
The prepared cGMP tracer should be stored at 4 ° C and valid for 4 weeks.
Tracer dye: Adding dye can aid visual observation, adding dye to the prepared tracer (60 ul of dye added to 6 ml of tracer or 300 ul of dye and 30 ml of tracer)
cGMP antiserum
100dtn cGMP antiserum with 6ml buffer
Or 500 dtn cGMP antiserum with 30 ml of buffer
The prepared cGMP antiserum should be stored at 4 ° C and valid for 4 weeks.
Anti-sera dyes: Adding dyes can aid visual observation, adding dye to the prepared antiserum (60 ul of dye added to 6 ml of antiserum or 300 ul of dye and 30 ml of antiserum)
Preparation of non-acetylated standards and samples
The cGMP standard was prepared in 1 ml of buffer at a final concentration of 300 pmol/ml and stored at 4 ° C for 6 weeks.
Standard preparation: Prepare 8 clean tubes, label, draw 900ul buffer to No.1 tube, 2-8 tube plus 500ul buffer, draw 100ul bulk standard (300 pmol/ml) to No.1 tube, mix, Pipette 500ul to tube No. 2 from the No. 1 tube, mix and dilute in sequence. The diluted standard storage time should not exceed 24h
As shown
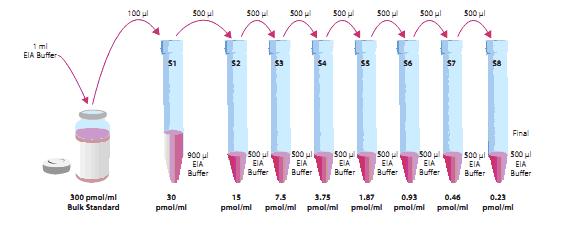
Preparation of the sample: If the sample requires purification, it is done according to the purification step, and if no purification is required, no further preparation is required. However, the sample needs to be diluted to ensure that its concentration remains within the linear error of the standard curve (20%-80% B/Bo).
Standard and sample preparation---acetylation
Preparation of the standard curve
Reconstitute standard cGMP with 1 ml of EIA buffer and pipet 100 μl of standard A to 9.9 ml of EIA at a concentration of 3 pmol/ml.
Note that if the sample is extracted by tissue extraction and cannot be analyzed with an EIA of at least 1:5, the TCA is extracted by ether extraction to prepare a standard curve. Any diluted sample needs to be processed in this way
Prepare the standard curve with EIA: Take 9 clean tubes and number #0 to #8, draw 900μl to #0 (only buffer), add #5 to #8 to 500μl EIAbuffer, and absorb 1ml standard B (3pmol/ml) to #1 Then, take 500μl to #2 to dilute, mix, then take 500μl from #2 to #3, mix, and so on, to #8, the diluent can not be stored for more than 24 hours.
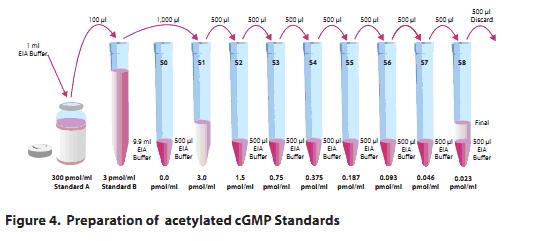
Sample preparation
If the sample requires purification, it is purified prior to acetylation (operations refer to the purification procedure of 12-14). Although purification is not required, we recommend purifying the sample to ensure the integrity of the assay. If the acetylated sample is less than 500 μl, a volume of KOH must be added, and an appropriate amount of anhydrous acetic acid.
KOH preparation
Dispose of 4M KOH solution, dissolve 100dtnKOH to 10ml of ultrapure water or 500dtn to 50ml of ultrapure water
Acetylation step (established in a 500μl system)
All standard samples in #0-#8 must be acetylated and each sample/standard must be acetylated separately. It is important to ensure acetylation under the same conditions. The difference in mixing time or the time of adding KOH will affect the test results.
500 μl of the sample, quickly add 100 μl of 4 M KOH and 25 μl of anhydrous acetic acid, mix for 15 s in a homomixer, add 25 μl of 4 M KOH and mix, repeat the same procedure for the remaining samples.
Note that if the sample contains less than 250 mM sugar, the volume of the appropriate KOH and anhydrous acetic acid should be increased to ensure complete reaction of acetylation.
General considerations
Pre-test samples are banned from organic solvents for pretreatment
Samples should be tested immediately after collection, but samples frozen at -80 °C should be thawed and not immediately detectable.
The recommended layout is as follows:
(The layout can be adjusted according to the actual situation of the experiment)
Note: Each slat contains 2 blank control wells (Blk), 2 non-specific wells (NSB), 2 maximum wells (B 0 ). 8 standard wells (double), as shown below Show:

Experimental procedure
A. Adding reagents
1. EIA buffer
Add 100 μl of EIA buffer to non-specific coated wells (NSB) and add 50 μl to the maximum well ( B 0 ). If the medium sample is added to dilute the standard curve, in non-specific coated wells (NSB) The neutralization maximal well (B 0 ) was added to 50 μl of the medium sample, and 50 μl of EIA buffer was added to the NSB well.
2. Standard products
Add 50 μl of the standard #8 to the S8 well. Add 50 μl of the test tube #7 to the S7 well. Add each standard to the appropriate well.
3. Sample
Add 50 μl of the sample to each well in turn, each sample has at least two dilution ratios. Each dilution ratio is parallelized.
4. Enzymes
Add 50 μl of enzyme conjugate to each well (except for TA and Blk wells)
5.cGMP antiserum
Add 50 μl of antiserum to the corresponding wells (TA and NBS wells, except for Blk wells)
Microporous | Buffer | Standard/sample | Tracer | antibody |
Blk | - | - | - | - |
TA | - | - | 5ul | - |
NSB | 100ul | - | 50ul | - |
B0 | 50ul | - | 50ul | 50ul |
Std/Sample | - | 50ul | 50ul | 50ul |
B. Incubation of the reaction plate
Incubate for 18 h at room temperature with a plastic film (No. 400012) cover plate (or 18 h at 4 ° C for a slight increase in test sensitivity)
C. The test continues
1. Reconstitute Ellman's reagent before use (20 ml of reagent is enough to add 100 test wells). One 100 dtn of Ellman's reagent (Cat. 400050) was reconstituted with 20 ml of ultrapure water. Note: Reconstituted Ellman's reagent is unstable and can only be used immediately and stored in the dark.
2. Discard the reaction solution in the reaction well and wash it 5 times with the washing solution.
3. Ellman's reagent 200ul is prepared for each reaction well.
4. Add 5 ul of tracer reagent to the TA well.
5. Using a plastic film cover, shake the reaction on a shaker for 60-90 minutes, if at 4 ° C, the time is about 90-120 minutes.
D. Reading board
1 Use a clean paper towel to wipe off the fingerprint on the bottom of the slat.
2 remove the plastic film, but avoid Ellman reagent sputtering
3 Reading at 405-420nm. It is recommended to read the sample value when the reading of B 0 hole is in the range of 0.3-1.0 AU (the value after subtracting the blank hole). If the value of each hole exceeds 1.5, the plate should be washed and added. Ellman reagent is incubated again
Retest.
1. OD mean of NSB holes
2. OD mean of B0 hole
3. B0 mean minus NSB mean, this is the corrected B0 or ​​corrected maximum binding
4. Calculate the %B/B0 (% sample or standard binding amount/maximum binding amount) value of the remaining micropores, the absorption value of S1 minus the absorption average of NSB, and then divide by the corrected B0 value and multiply by 100 to obtain %B/B0,
The remaining standards and samples were repeatedly calculated in this way.
Drawing of standard curves
The curve is plotted on the X-axis with the %B/B0 value of the standard as the Y-axis and the concentration of cGMP, and the data is substituted into the four-parameter equation.
Calculate the %B/B0 value of each sample and calculate the concentration of the sample based on the equation of the standard curve. A sample with a %B/B0 value greater than 80% or less than 20% is considered to be outside the linear range of the standard curve and needs to be redone. The results obtained by different dilution ratios of the same sample are quite different, indicating infection and purification.
This translation is for reference only. If you have any questions, please refer to the original manual!
Exclusive distributor in China: Shenzhen Kerunda Bioengineering Co., Ltd.
Address: 6th Floor, No. 10, Yanshan Road, Shekou, Shenzhen
Telephone, 26680196 fax
Free order phone number: 518067
Nursing pad is a disposable sanitary product made of PE film, non-woven fabric, fluff pulp, polymer and other materials.
Adult nursing pads are mainly used for people who have undergone surgery, those who are paralyzed, and those who cannot take care of themselves. The adult nursing pad is easy to replace, which can ensure that the mattress under the building will not be soiled.
Disposable Underpads,Assurance Underpads,Disposable Underpads Bulk,Disposable Bed Underpads
Shandong Kangshun Daily Products Co., Ltd , https://www.centurybenifit.com