Release date: 2016-05-16
About 20 years ago, Professor Bob Pilliar began looking for alternative materials for synthetic bone. At one time, plastics, metals, and ceramics were once thought to be the newest and best materials available for joint replacement, but they have a premise for the pain relief and mobility of patients, that is, these materials are not durable. Pilliar is known as the father of Canadian ceramic materials.
Today, by working with two other researchers, Pilliar, an emeritus professor at the University of Toronto School of Dentistry and Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering, has found the natural ingredients that can be used to make future implants. To replace the artificial knee and hip joints, his parts must be biodegradable, durable and tailored to the patient's characteristics.
In the end, the researchers found an effective formula in the form of calcium phosphate. The powder is made up of the same mineral components as human bones, and it comes from a degradable biomaterial that Monsanto, a US seed giant, has abandoned. After some research, Pilliar and his colleagues believe that they have found the right compound to create a bone substitute material, after which all they need is to find the right manufacturing method.
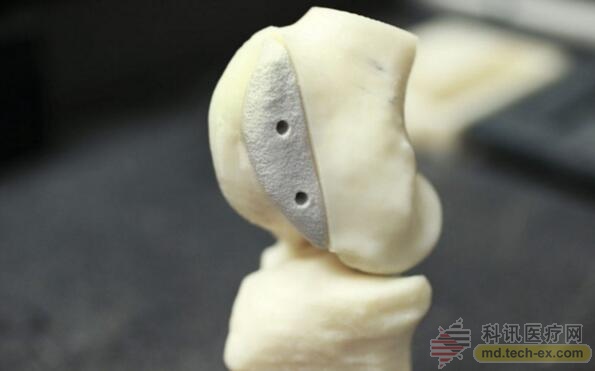
To this end, a young mechatronics engineer Mihaela Vlasea took over the task. She is a master in the field of additive manufacturing. Based on the characteristics and requirements of this material, she developed a custom 3D printer. According to Tiangong, this equipment is as large as a two-door refrigerator, which uses ultraviolet light to bond calcium phosphate powder together. Using this machine, Vlasea manufactures pipes and cavities inside the implant with tip-sized precision.
To put it bluntly, this 3D printed bone implant is like an anthill, the interior of which is filled with a network of pipes for transporting nutrients, and the exit of this network is a small hole in the surface of the implant. Once implanted, the human bone cells are spread and mechanically interlocked with the bone structure.
"The way we arrange the pores inside the part basically allows the natural bone to grow at different rates within the implant," she said, adding that the method can also be applied to the design of fuel cells and dental implants.

Over time, calcium polyphosphate is absorbed by the body, and the patient's tissues and cells grow into the shape of artificial implants. "We hope to use it instead of artificial joints, and to ask for all the metal materials. But in the short term, we can only try to replace the small bones," Professor Pilliar said. "If we succeed, try it further to create larger joints.
In addition, Professor Pilliar is also developing alternatives to human cartilage, which, if successful, is a boon for many arthritis patients.
Unlike our common sense, arthritis patients are actually not limited to the elderly in the city. The disease is mainly caused by trauma, deformed joints or sports injuries. At present, because chondrocytes cannot be regenerated, the treatment for it is very limited.
"Now, if the joint is damaged, there is no real treatment that can stimulate it." Rita Kandel, director of pathology and laboratory medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital: "In the end, you can only rely on metal and plastic materials. a substitute."
As one of the three main investigators of this skeletal project, Kandel has worked with Professor Pilliar and researcher Marc Grynpas of the University of Toronto for more than two decades.
According to her, today's uniform-sized implants have a service life of 20 to 30 years, after which surgery is required to replace the new implant. Kandel hopes to solve this problem by using the "biological joint replacement" created by the patient's own tissues and cells.
To this end, Kandel attempts to extract stem cells from the patient's bone marrow and then recode them in the laboratory to grow into immature chondrocytes. The cells matured after a few weeks, and the researchers stacked them on the 3D printed calcium phosphate implant at the University of Waterloo and allowed it to grow. According to Tiangong, once the implant is implanted into the body through surgery, it can naturally function and even heal itself.
Kandel calls it "biological resurfacing," which further reduces the likelihood that the implant will undergo a rejection reaction after implantation in the human body. "If you use the patient's own cells, they won't be considered foreign by the human body." She said and added that this new treatment can fundamentally prevent the development of arthritis.
Although the possible price of this custom implant is still unknown, Kandel expects the product to be cheaper after commercialization because of the low price of raw materials used. In addition, she estimates that such new types of artificial joint "bioreplacements" will be widely used in the next decade.
At the same time, researchers are testing the feasibility of using this new method to repair small bone substitutes through animal testing, which they expect will continue for two years.
(Compiled from Toronto Star)
Source: Tiangongshe
Fruit juice drinks is a beverage made of fruit juice products obtained by physical methods such as pressing, centrifugation and extraction. Fruit juice retains most of the nutrients in the fruit, such as vitamins, minerals, sugar and pectin in dietary fiber. Often drinking fruit juice can help digestion, moisten the intestines and supplement the lack of nutrients in the diet.
There are two kinds of fruit juice: pure fruit juice and compound fruit juice. As far as pure fruit juice is concerned, it can be divided into two types: one is to directly use the original juice, and the other is to dehydrate the freshly squeezed fruit juice first, and then add water to reduce it into concentrated fruit juice. Most pure fruit juices are concentrated. AGOLYN offers various flavors of honey tea, such as honey Citron tea etc.
Juice Drinks,Honey Tea,Honey Citron Tea,Goji Berry Juice
Xi'an Gawen Biotechnology Co., Ltd , https://www.seoagolyn.com