--- The production of special biological organic-inorganic compound fertilizers to improve and extend the fertilizer efficiency are important measures. 1. Pollution status of chemical fertilizers Recent research shows that through surface runoff, nitrogen and phosphorus emitted from farmland and nitrogen that enters groundwater through land leakage and The release of nitrogen from the farmland to the atmosphere in gaseous form has become one of the important sources of pollution for water bodies and the atmosphere. Before the 1980s, the total input of organic manure and chemical fertilizers in farmland in China was negative compared with the total output (nutrition taken from crops). After 1980s, nitrogen and phosphorus accumulation in farmland soil increased dramatically due to the large amount of nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizer application. In 1995, farmland accumulated 3.5 million tons of nitrogen and 4.49 million tons of phosphorus (P2O5). The transfer of nitrogen and phosphorus from farmland soil to enclosed or semi-enclosed lakes, reservoirs, rivers, and bays will result in the eutrophication of these waters. Nitrogen and phosphorus are known to be the most important nutritional factors for eutrophication. When the phosphorus in the water reaches PO4-P 0.015 ml/l and the inorganic nitrogen content is greater than 0.2 ml/l, "algal bloom" phenomenon may occur, and red tide appears in the estuary and bay. Increased nitrogen concentration will have an effect on the eutrophication of water bodies. Once the eutrophication of water bodies occurs, it will directly affect the quality of water supply for industrial and agricultural water supply and human drinking water, threatening human health and aquaculture.
The sources of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrition in lakes are nothing more than industrial wastewater, domestic sewage, farmland runoff and lake aquatic feed inputs. From the analysis of existing data, the results of extensive use of N and P fertilizers, the N and P that migrated from farmland runoff to lakes, accounted for a relatively high proportion of the total N and P load in lakes, where P was the percentage of total lake P load from farmland surface runoff. The percentage above nitrogen is nearly doubled. It can be seen that phosphorus in farmland surface runoff threats lake eutrophication even more than nitrogen.
Many research results at home and abroad show that both the increase of nitrate concentration in surface water and groundwater are related to the increase of nitrogen fertilizer application in farmland. China's total nitrogenous fertilizer application ranks first in the world. According to statistics from the field trials of fertilizers nationwide since 1980, according to the Institute of Geography of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the average utilization rate of nitrogen fertilizers in China is 35%. Some of the nitrogen that is not absorbed by the crop is stored in the soil and absorbed by the soil. Some of it is lost in gaseous form. A considerable amount of nitrogen enters the groundwater in the form of nitrate (NO3-) through microbial nitrification and becomes an important source of pollution. .
In the 20th century from 1972 to 1982 in the suburbs of Beijing, the increase in the application of chemical nitrogen fertilizer in the cultivated land of 6 million mu in 10 years was similar to the increase trend of groundwater nitrate concentration. According to sampling and analysis of groundwater and drinking water in 69 towns and towns in the Jingjintang area of ​​the Soils Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, more than half of the nitrate content exceeds the drinking water standard (≥50 mg/L). In 76 drinking water wells in 16 counties in Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Shanghai in the Taihu Basin, the over-standard rates of nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen were 38.2% and 57.9%, respectively. Those areas where groundwater nitrates are severely excessive are the areas with excessive nitrogen fertilizers.
According to reports in the literature, 80% of the nitrates consumed by the human body come from vegetables, so the level of nitrate in vegetables has been directly related to the intake of human nitrates and human health. According to the investigation of nitrate levels in 33 kinds of vegetables in Shanghai, most of the vegetables consumed by residents in Shanghai in the year are grade 3 (with nitrate content greater than 1,440 mg/kg) and grade 4 (with nitrate content greater than 3,100 mg/kg), indicating that Shanghai The nitrate content in vegetables used by residents in the area has reached a critical level or exceeded a critical level. The nitrate content in edible vegetables is seriously exceeded, and it is related to excessive nitrogen fertilizer application in vegetable fields. According to the investigation of the amount of fertilizer applied in 23 vegetable plots in Haidian District of Beijing, the average nitrogen content of vegetables per season was as high as 780 kg/ha, which was several times higher than the nitrogen requirement of vegetable crops. According to a survey conducted by Shouguang City, a major vegetable producing area in Beijing, the average nitrogen (N) content of 11 greenhouse vegetables in the area was 1804.2 kg/ha, phosphorus (P2O5) was 968.8 kg/ha, and potassium (K2O) was 740 kg/ha, far exceeding the amount of fertilizer needed for vegetables. Excessive fertilization resulted in a decline in the quality of the vegetables. The nitrate content exceeded the standard of food consumption, which also led to the impediment of soil salt concentration. After many greenhouses were planted continuously for three to four years, the secondary boronized vegetables had to be replaced due to the decrease of secondary salinized vegetables. According to the author's investigation on the vegetable fields in the suburbs of Changchun, some vegetable farms in the area of ​​Xingfu Township could not continue to grow vegetables due to over-fertilization of secondary soil salinization. The farmers did not know why. The problem was quite serious.
II. Continuing to improve the adverse consequences of nitrogen and phosphorus content in inorganic compound fertilizers (one-time application type) At present, some of the compound fertilizer manufacturers in China are adapting to farmers' “one-shotâ€
(One-time fertilization, no top-dressing) Fertilizer requirements, blindly increase the content of nitrogen in the compound fertilizer (some increase the nitrogen content to 28%), phosphorus, potassium are also relatively increased, and some will total nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium content To 65% or more, to ensure that the crop growth and development will not be deferred later. In fact, this approach is very unscientific, first of all, some manufacturers in the process with large-scale long-acting urea, the use of drum or disk granulation, the added urea can not be completely crushed and difficult to fully mixed with sustained-release, long-acting agents, carriers, etc. For the purpose of achieving long-term effects, it is very difficult to maintain the fertilizer effect for 120 days with dicyandiamide alone. In the past two years, the author has surveyed areas north of the Yellow River. Most of the high-yield "one-shelled bombardment" inorganic compound fertilizer crops have grown late. De-fertilization is not welcomed by users; in addition, the higher the nutrient content of compound fertilizers is, the lower the nutrient utilization rate is, and the heavier the residues and pollution are; the second is the imbalance in the nutrient combination ratio, and some manufacturers increase the content and reduce the cost. Increase the price of adding a lot of phosphorus and potassium, especially potassium chloride. There are three problems with this, and one is ineffective. Since the 1970s, China has continuously applied large quantities of diammonium phosphate, NPK complex compound fertilizers. Phosphorus and potassium in the soil have been relatively lacking. Nutrient analysis indicates that The northern soil has been relatively rich in phosphorus, and it does not require continuous application of phosphorus, especially large amounts of phosphorus. Regarding potassium, the soil in northern China is potassium- and potassium-preserving from the perspective of soil-forming parent materials. For years, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium ternary compound fertilizers have been used (high-content ternary compound fertilizers generally have high potassium content). Potassium is relatively scarce, and it is not necessary to plant potassium fertilizers to grow special potassium-promoting crops. Second, it is harmful. Phosphorus is more effective than zinc and other two-valence elements. It will cause many kinds of crops to suffer from nutrient deficiency, etc. Physiological diseases, such as white flower disease of corn, bacterial blight of rice, and small fruit disease of some fruit trees, result in reduced production. The soil science has long believed that more potassium in the soil can increase the effectiveness of nitrogen. However, since the 1970s, the author has conducted multi-year, multi-point balanced fertilization experiments of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in the black soil area in the black soil region. The occurrence of high potassium application at the point of production reduction may be due to the fact that potassium ions (K+) excessively affect the absorption of ammonium ions (NH+) by crops and reduce the effectiveness of nitrogen fertilizers. Crops have an excessive effect on excessive absorption of nutrients. Nitrogen accumulates more nitrates and nitrites, especially in vegetables and fruits. In the discovered carcinogens, there are nitrates and nitrites. Secondary ammonia is the strongest. 80% of the nitrates and nitrites accumulated by the human body come from vegetables. The nitrate and nitrite contents of vegetables in Beijing, Shanghai's suburbs, and Shouguang, Shandong's large and medium-sized cities have all exceeded the standards. All of them have unknowingly affected human health. The application of phosphate fertilizers to increase the accumulation of organic phosphorus (water eutrophication) in closed, semi-enclosed bodies of water and groundwater is also a serious hazard to humans and livestock. It seems that scientific and rational fertilization should arouse people’s attention; It is based on the content of nutrients and the effectiveness of carrier additives to determine the price, and the excess phosphorus and potassium nutrients shall be included in the cost to be paid by the consumer. Although the excess phosphorus can be converted into slow-acting phosphorus and difficult to re-use phosphorus, the effect is much worse, and excess potassium is lost. Farmers spent money without benefit, calling it invalid, harmful, and wasteful fertilization.
3. Develop and produce bio-organic and inorganic compound fertilizers to increase fertilizer nutrient utilization, extend fertilizer efficiency, promote crop yield increase, protect resources, protect the environment, and achieve the quantity, proportion, and nutrient absorption of N, P, and K elements in different crops for sustainable development. The morphology is not only different, but also varies greatly. For example, the ratio of N, P, and K for special fertilizers for Tian Wangwang melons is 12:6:12, while that for potato is 9:5:16. Application practice shows that these two different proportions are suitable for these two crops. The effect of increasing fertilizer production and compound fertilizer mainly depends on the content, proportion, and form of N, P, and K nutrients. According to the specific needs of different crops, special-purpose biological organic-inorganic compound fertilizers are produced, and full use of microorganisms, organic-inorganic composite colloids, multiple-combination conditioners, humic acid chelation, and other effects of increasing fertilizers, maintaining fertilizers, activating and slow release, etc. Improve and extend fertilizer efficiency. The application effect in the past two years shows that the appropriate nutrient quantity (content) and proportion are determined according to the needs of different crops. The appropriate nutrient form and conditioner type are selected. Nitrogen is added up to 18% and phosphorus is added to 7%. The nutrient utilization rate of organic-inorganic compound fertilizers increased to about 60%, and the fertilizer effect period was extended to about 120 days. The late-stage crops are not de-fertilized, live stalks are ripe, and the grain is full. The yield, benefit, quality and flavor are good, and it is welcomed by users.
T-Fiberglass Beams is our company's high-quality livestock used slat flooring system support equipment, which is a kind of Fiberglass Beams, it looks like the letter "T" from the side. Made of a special antifreeze, high temperature material, ranging in size from 110mm to 120mm, with ruggedized features. T-fiberglass Beams installation and use of very convenient, is a very good agricultural farming equipment. We can produce according to your special requirements, can also be produced according to your drawings. Our commitment to our products, our T-fiberglass beams are of high quality and easy to use. Looking forward to your patronage.
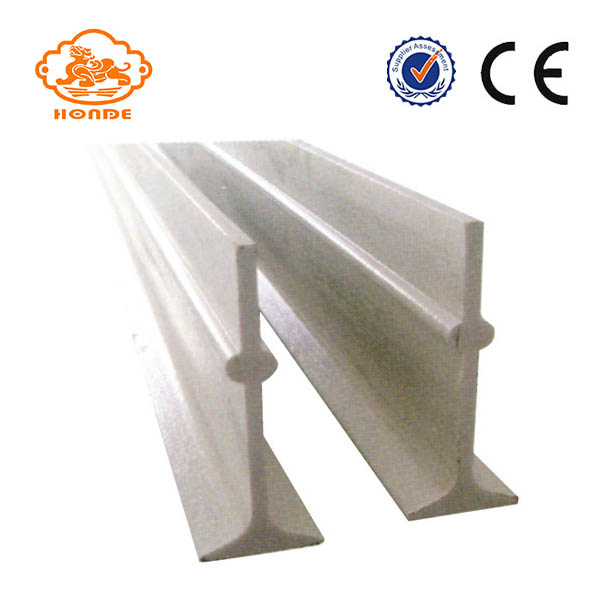
T-fiberglass Beams
T-Fiberglass Beams,Durable T-Fiberglass Beam,T-Fiberglass Beam For Farrowing Crates,Strong T-Fiberglass Beam
HuangHua FengYi Honde Metal Factory , https://www.farrowingcratesfromchina.com